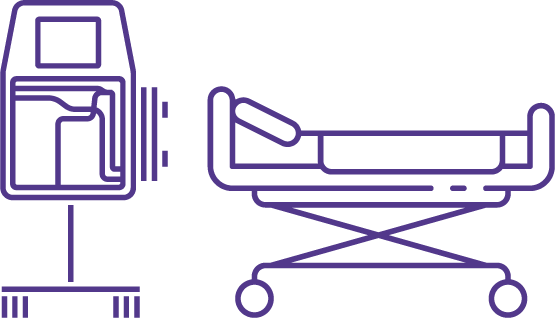
Continuous Renal Replacement Therapies (CRRT)
CRRT is a routine therapeutic tool in intensive care settings with more than 100’000 treatments performed worldwide every year.
SCUF
Slow Continuous UltraFiltration
in case of
Fluid overload
Congestive heart failure
Acute renal failure
SCUF is usually performed from 4 to 24 hours, until the targeted water level within the patient is reached.
SCUF is used to remove water from the body in cases of fluid overload. Thus, it is used both to reduce pressure within the body, especially on the heart, and to remove water that has cumulated within some organs, such as the lungs where oedemas form.
Technically speaking
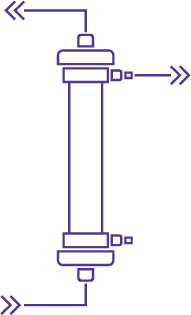
In SCUF, blood is passed through a hemofilter which allows water to be filtrated along with some other substances which are not of relevant importance in this case. The water is removed at a rate that is well tolerated by the patient and there is no compensation for the few undesired small losses of other substances.
CVVH
Continuous Veno-Venous Hemofiltration
in case of
Fluid overload
Congestive heart failure
Acute renal failure
Crush syndrome
Lactic acidosis
This therapy is usually performed continuously 24/7 until the renal function recovers, which may take from 2-3 days and up to 2-3 weeks.
CVVH is used to remove all of the substances that would normally be cleared by the kidneys; such as water, urea, creatinine and salts, as well as medium size molecules which result from cellular injury and are often nephrotoxic.
Technically speaking
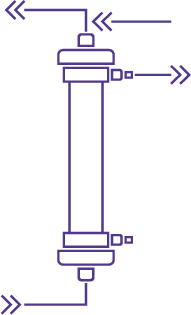
In CVVH, blood is passed through a hemofilter which allows water to be filtrated together with other relevant substances, such as salts, urea, creatinine or other medium size substances. The resulting fluid is called ultrafiltrate. Ultrafiltrate is removed at a rate which provides the necessary clearance of the desired substances. As this clearance rate is often too high for some other substances, a substitution fluid is injected in the blood to compensate for undesired losses, such as that of water.
CVVHD
Continuous Veno-Venous HemoDialysis
in case of
Acute renal failure
Lactic acidosis
It is a therapy that is usually performed continuously 24/7 until the renal function recovers, which may take from 2-3 days and up to 2-3 weeks.
CVVHD is used to remove the substances that are the most commonly cleared by the kidneys; such as water, urea, creatinine and salts. It also has some ability to remove the medium size molecules which result from cellular injury, however with less efficiency than CVVH.
Technically speaking
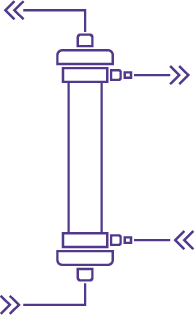
In CVVHD, blood is passed through a dialyzer, while dialysate is circulated on the other side of a semi-permeable membrane. The concentration difference of small molecules across the membrane will tend to equilibrate which is called diffusion or osmosis. In particular the substances to be removed from the blood will migrate into the dialysate and the drained dialysate will take them away. The removal of water is added to the diffusion process by extracting more drained dialysate than the quantity of fresh dialysate injected, the difference of volume being water removed from the blood by filtration.
CVVHDF
Continuous Veno-Venous HemoDiaFiltration
in case of
Fluid overload
Congestive heart failure
Acute renal failure
It is a therapy that is usually performed continuously 24/7 until the renal function recovers, which may take from 2-3 days and up to 2-3 weeks.
CVVHDF is a combination of hemofiltration and hemodialysis which may be preferred to either modality alone. Reasons for this can be, for example, the higher clearance of medium size substances when compared to hemodialysis or less dependence on blood flow when compared to hemofiltration.
Technically speaking
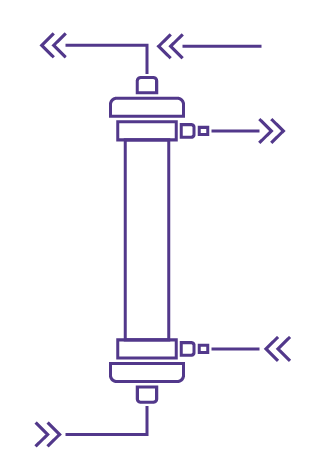
In CVVHDF, blood is passed through a hemofilter while dialysate is injected on the other side of a semi-permeable membrane. During treatment a significant amount of ultrafiltrate is extracted from blood thus combining the filtration process and the dialysis one. In CVVHDF, substitution fluid must be injected in the blood to compensate for the filtration flow.
A bit of
HISTORY
CRRT is a routine therapeutic tool in intensive care ; its story has started during the seventies.
In 1977, Dr. Peter Kramer was the first person to describe a CRRT type therapy in the literature. It was named CAVH (Continuous Arterio-Venous Hemofiltration) because the blood was moved from an artery to a vein through a hemofilter. Ultrafiltration rate was controlled by raising and lowering the drain bag which allowed for modification of the transmembrane pressure (TMP).
Because of the hypotension experienced by critically ill patients, the blood flow of the AV method, where the difference in pressure between arteries and venous vessels is used to create the flow, is low and limits the volume of ultrafiltrate which can be obtained.
In 1982 the US FDA (Food and Drug Administration) approved CAVH.
From the early 80’s a blood pump and a double-lumen catheter in a large vein are used to provide a consistent blood flow, and therefore ultrafiltration flow. This so called Veno-Venous technique has since been adopted and improved to become the standard in CRRT.
In the 90’s the first fully automated machines are made available and immediately become popular in the intensive care setting.
Since the beginning of the millennium, technology has been improved to achieve better clinical outcomes and reach higher safety levels for patients. With this philosophy in mind, Infomed has designed devices which:
- Perform higher flows thus higher clearances
- Allow new therapies such as CPFA
- Optimise the blood flow,
- Display treatment values overtime on graphs
In 2002, the ADQI (Adequate Dialysis Quality Initiative) group gives the first consensus definition of ARF (Acute Renal Failure), the main reason to perform CRRT. Later the term AKI (Acute Kidney Injury) has appeared as a synonymous.
Hot topics

ERA 2026
Join us to the 63th European Renal Association (ERA) Congress in Glasgow, Scotland. ERA is based on 3 pillars: Education, Science and Networking. As Infomed, we support the association for more than 20 years and we clearly appreciate to be a key partner to the association to develop excellence and quality of the scientific knowledge.

EDUCATIONAL VIDEOS
Discover Infomed’s educational videos with presentation from basics of blood purification to internationally renowned professor physician’s interview and discover all the interest of various application of therapeutic technics offered by Infomed’s solutions.

Kidney Week Denver
Come and share with us the Kidney Week organized by the American Society of Nephrology (ASN), in November in Denver, Colorado. This key event is focus on education, training and knowledge sharing, through a large number of publications. Once again, we are pleased to support and take part by supporting the exchange of the international know-how in the field.